Modular Solutions: Revolutionizing Lab Construction
Laboratories are the backbone of scientific research, where groundbreaking discoveries and innovations are born. As the demand for research facilities continues to grow, traditional construction methods face challenges in meeting the evolving needs of modern laboratories.
In response, modular construction has emerged as a game-changing solution, revolutionizing the way laboratories are designed and built.
In this blog, we will explore the concept of modular solutions in lab construction, the benefits they offer, and how they are reshaping the future of scientific research facilities.
Understanding Modular Construction
Modular construction involves creating prefabricated building components, known as modules, in a controlled factory environment. These modules are then transported to the construction site and assembled into the final structure.
In the context of laboratory construction, modular solutions offer a flexible and efficient approach to create state-of-the-art research facilities.
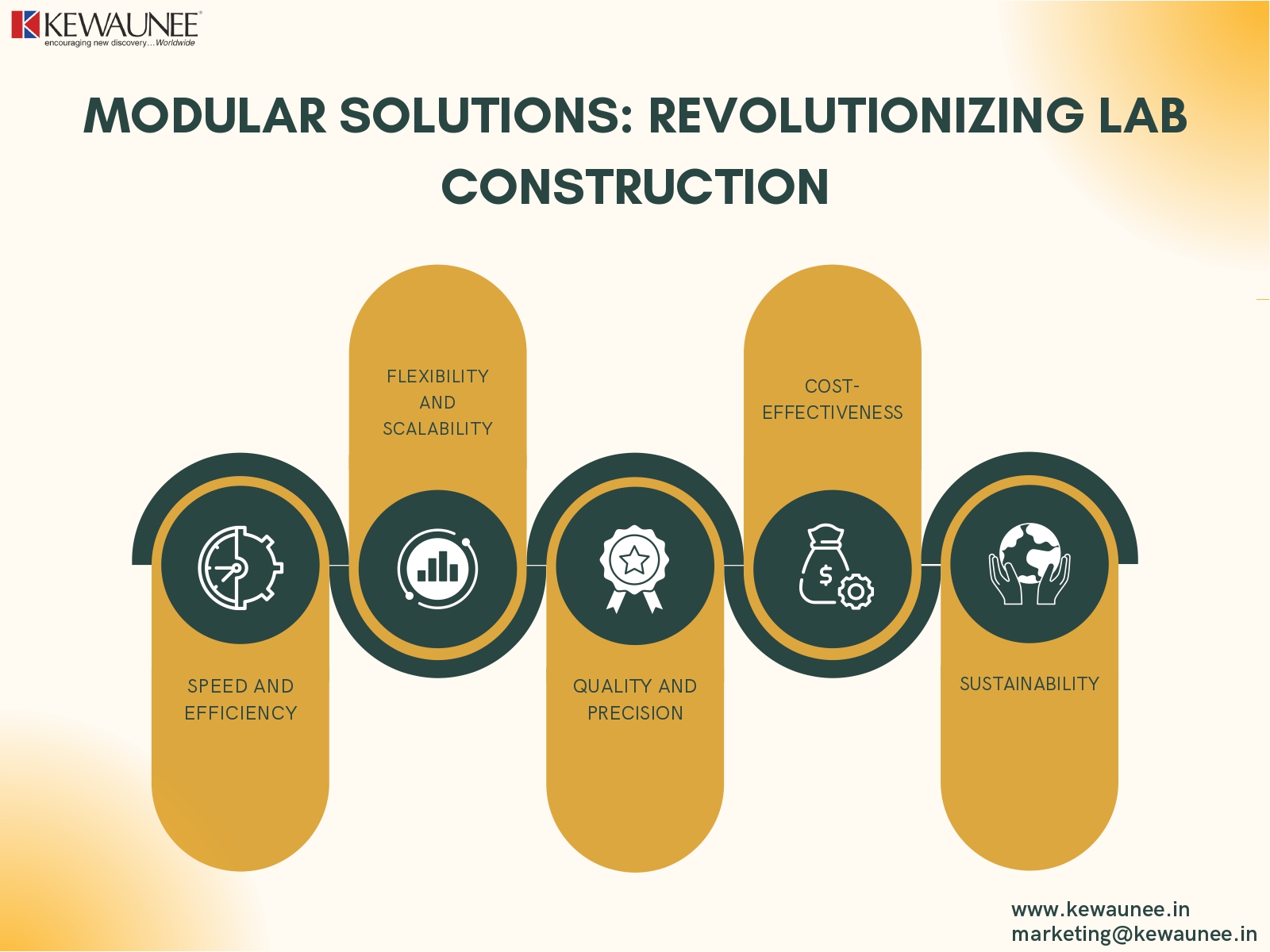
The Advantages of Modular Solutions in Lab Construction
- Speed and Efficiency: Modular construction significantly reduces the construction timeline. By simultaneously manufacturing modules off-site and preparing the site, project completion can be accelerated by up to 50%. This speed advantage is especially crucial for research facilities where time-sensitive experiments and studies are conducted.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Modular labs can be easily expanded, reconfigured, or relocated to accommodate changing research needs. Researchers can quickly adapt the laboratory space to support new projects or research priorities without the complexities and costs associated with traditional renovations.
- Quality and Precision: Factory-controlled environments ensure consistent quality in module construction. Precise engineering and quality control lead to reliable structures that meet stringent safety and regulatory standards, providing a safe and secure environment for researchers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Modular construction is generally more cost-effective than conventional construction. Reduced construction time, lower labor costs, and minimized material waste contribute to overall project savings.
- Sustainability: Prefabricated modules can be constructed with eco-friendly materials, and modular construction generates less construction waste compared to traditional methods. Additionally, the flexibility to add or remove modules allows for energy-efficient space management.
Customization for Specific Research Needs
One of the most remarkable aspects of modular solutions is their adaptability to cater to specific research requirements.
- Laboratory Types: Modular solutions can accommodate various types of laboratories, including wet labs, cleanrooms, biological containment labs, and more. Customized layouts and features are tailored to the specific research conducted within each lab.
- Specialized Equipment Integration: Modular labs can be designed to seamlessly integrate with specialized equipment and instrumentation, ensuring efficient workflows and optimal utilization of space.
- Safety and Compliance: Modular labs can be constructed to meet strict safety and regulatory requirements, including ventilation standards, chemical containment, and biosafety measures.
- Additional Amenities: Modular solutions can incorporate additional amenities such as office spaces, meeting rooms, and break areas, providing a comprehensive research environment.
Innovative Design and Technology Integration
Modular solutions are not limited to conventional laboratory designs. They offer an opportunity for cutting-edge design and technology integration.
- Smart Laboratories: Modular labs can be equipped with smart technologies, including IoT sensors for environmental monitoring, automated controls for ventilation, and energy-efficient lighting systems.
- BIM (Building Information Modeling): BIM technology allows for detailed virtual modeling of the laboratory layout, enabling researchers and architects to visualize and optimize the lab design before construction.
- Sustainable Materials and Systems: Modular labs can be constructed with eco-friendly materials, incorporating energy-efficient HVAC systems, solar panels, and rainwater harvesting solutions.
Challenges and Considerations
While modular solutions offer numerous benefits, certain challenges and considerations should be taken into account:
- Customization Complexity: Highly specialized research requirements may require intricate customization, which can add complexity to the modular construction process.
- Site Readiness: Adequate site preparation and utilities installation are essential to ensure a smooth and timely modular construction process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Modular labs must meet the same regulatory standards as traditionally constructed labs. Coordination with regulatory authorities is critical to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Modular solutions have ushered in a new era of efficiency, flexibility, and innovation in lab construction. By offering accelerated timelines, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to adapt to evolving research needs, modular labs are revolutionizing scientific research facilities.
The combination of customization, advanced design, and technology integration makes modular solutions an attractive option for researchers and institutions seeking to stay at the forefront of scientific discoveries.
As the demand for state-of-the-art laboratories continues to grow, modular construction is poised to shape the future of scientific research in the most efficient and sustainable manner.
Comments are closed.